Terzaghi’s bearing capacity theory
Terzaghi’s bearing capacity theory is useful to determine the bearing capacity of soils under a strip footing. This theory is only applicable to shallow foundations. He considered some assumptions which are as follows.
- The base of the strip footing is rough.
- The depth of footing is less than or equal to its breadth i.e., shallow footing.
- He neglected the shear strength of soil above the base of footing and replaced it with uniform surcharge. (
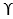 Df)
Df) - The load acting on the footing is uniformly distributed and is acting in vertical direction.
- He assumed that the length of the footing is infinite.
- He considered Mohr-coulomb equation as a governing factor for the shear strength of soil.
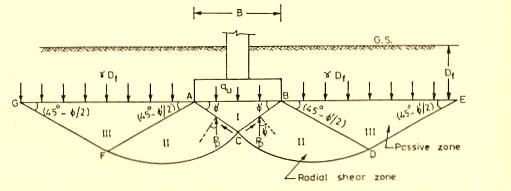
As shown in above figure, AB is base of the footing. He divided the shear zones into 3 categories. Zone -1 (ABC) which is under the base is acts as if it were a part of the footing itself. Zone -2 (CAF and CBD) acts as radial shear zones which is bear by the sloping edges AC and BC. Zone -3 (AFG and BDE) is named as Rankine’s passive zones which are taking surcharge (y Df) coming from its top layer of soil.
From the equation of equilibrium,
Downward forces = upward forces
Load from footing x weight of wedge = passive pressure + cohesion x CB sin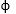
Where Pp = resultant passive pressure = (Pp)y + (Pp)c + (Pp)q
(Pp)y is derived by considering weight of wedge BCDE and by making cohesion and surcharge zero.
(Pp)c is derived by considering cohesion and by neglecting weight and surcharge.
(Pp)q is derived by considering surcharge and by neglecting weight and cohesion.
Therefore,
By substituting,
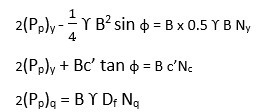
So, finally we get qu = c’Nc + y Df Nq + 0.5 y B Ny
The above equation is called as Terzaghi’s bearing capacity equation. Where qu is the ultimate bearing capacity and Nc, Nq, Ny are the Terzaghi’s bearing capacity factors. These dimensionless factors are dependents on angle of shearing resistance.
Equations to find the bearing capacity factors are:

Where
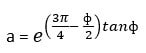
Kp = coefficient of passive earth pressure.
| Nc | Nq | Ny | |
| 0 | 5.7 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 7.3 | 1.6 | 0.5 |
| 10 | 9.6 | 2.7 | 1.2 |
| 15 | 12.9 | 4.4 | 2.5 |
| 20 | 17.7 | 7.4 | 5 |
| 25 | 25.1 | 12.7 | 9.7 |
| 30 | 37.2 | 22.5 | 19.7 |
| 35 | 57.8 | 41.4 | 42.4 |
| 40 | 95.7 | 81.3 | 100.4 |
| 45 | 172.3 | 173.3 | 297.5 |
| 50 | 347.5 | 415.1 | 1153.2 |
Finally, to determine bearing capacity under strip footing we can use
qu = c’Nc + 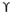 Df Nq + 0.5
Df Nq + 0.5 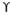 B Ny
B Ny
By the modification of above equation, equations for square and circular footings are also given and they are.
For square footing
qu = 1.2 c’Nc + 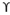 Df Nq + 0.4
Df Nq + 0.4 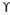 B Ny
B Ny
For circular footing
qu = 1.2 c’Nc +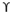 Df Nq + 0.3
Df Nq + 0.3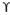 B Ny
B Ny
No comments:
Post a Comment